

Predicting operational efficiency or return on assets.Įarnings yield is defined as the ratio of net income to price, or the reciprocal of the price-earnings ratio. For large firms, earnings yield is particularly effective in To measure the productivity of capital through economic value added is For small firms, the ability of earnings yield It may be concluded that earnings yield measures multipleĭimensions of financial performance for firms of different size and volatility Survival, while large retailers borrow against large-scale investments inĪssets, as shown by the significant explanation of the equity multiplier byĮarnings yield. Product lines emphasizing return on assets or being operationally efficient for Retail is in retrenchment with small retailers selling traditional
Return on equity software#
Similar results were obtained for the computer software In large biotechnology firms, earnings yield was significantly related Risk demonstrating the explanation of return on assets by earnings yield, whileĮarnings yield is significantly related to economic value added for high market riskįirms. Market risk demarcates small biotechnology firms with those with low market Operational efficiency through higher return on assets and return on equity. Risk firms, or drillers using the new shale rock techniques strove for drillers in new locations with existing technology, found thatĮarnings yield was related to all outcome measures, while large, high-market Low market risk and high firm-specific risk, i.e. In the oil and gas industry, small producers with Nonlinear relationships between earnings yield and all outcomes with Yield on return on assets was predictable with linear relationships andĪutocorrelated residuals, while that for small firms was unpredictable with Multiplier beyond book value and book to market. NASDAQ stocks from 2010-2014, earnings yield significantly explained return on TheĪnalysis is conducted both across industries and within the oil and gas,Ĭomputer software, biotechnology and retail industries. Multiplier are determined for firms of different size and volatility.
Return on equity full#
The full sample, the differential effects of earnings yield on return onĪssets, return on equity, stock returns, economic value added and the equity It excludes the irrationality that can confound market-based measures ofĪ firm’s ability to earn profits as the indicator of superior performance. Companies may have bonds payable, leases, and pension obligations under this category.This study identifies earnings yield as a measure ofįinancial performance that is based on a firm’s ability to sell profitable Long-term liabilities are obligations that are due for repayment over periods longer than one year. This includes accounts payable (AP) and any outstanding taxes. Total liabilities consist of current and long-term liabilities.Ĭurrent liabilities are debts typically due for repayment within one year. They include investments property, plant, and equipment (PPE), and intangibles such as patents. Long-term assets are possessions that cannot reliably be converted to cash or consumed within a year. Current assets include cash and anything that can be converted to cash within a year, such as accounts receivable and inventory. Total assets include current and noncurrent assets.
The balance sheet holds the data needed for the accounting equation. This formula is also known as the accounting equation or the balance sheet equation. S ha re h o l d er Eq u i t y = T o t a l A sse t s − T o t a l L iabi l i t i es Shareholder Equity = Total Assets - Total Liabilities

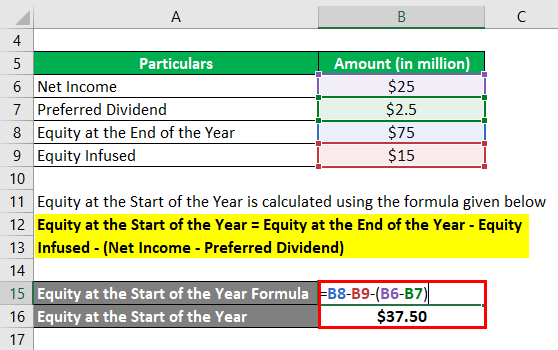
You can figure out the total SE of a company using the following formula: The Formula for Calculating SEĪll the information needed to compute a company's shareholder equity is available on its balance sheet. If the company ever needs to be liquidated, SE is the amount of money that would be returned to these owners after all other debts are satisfied. That is, it is the dollar value of the company to its owners. Shareholder equity represents the total amount of capital in a company that is directly linked to its owners.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
